Gravitational Waves from Axisymmetric, Rotational Stellar Core Collapse- Gravitational Wave Signature Data - |
| Christian D. Ott (cott@as.arizona.edu), Adam Burrows (burrows@astro.princeton.edu), Eli Livne (eli@phys.huji.ac.il), Rolf Walder (rwalder@astro.phys.ethz.ch) |
Astrophysical Journal, 600, 834 (2004).
Abstract
|
We have carried out an extensive set of two-dimensional, axisymmetric,
purely-hydrodynamic calculations
of rotational stellar core collapse with a realistic, finite-temperature
nuclear equation of state and realistic massive star progenitor models.
For each of the total number of 72 different simulations we performed,
the gravitational wave signature was extracted via the quadrupole formula in the
slow-motion, weak-field approximation.
We investigate the consequences of variation in the initial ratio of
rotational kinetic energy to gravitational potential energy and in the initial degree of
differential rotation. Furthermore, we include in our model suite progenitors from
recent evolutionary calculations that take into account the effects of rotation
and magnetic torques. For each model, we calculate gravitational
radiation wave forms, characteristic wave strain spectra,
energy spectra, final rotational profiles, and total radiated energy.
In addition, we compare our model signals with the anticipated sensitivities
of the 1st- and 2nd-generation LIGO detectors coming on line. We find that
most of our models are detectable by LIGO from anywhere in the Milky Way.
|
| Electronic journal article: | ApJ 600, 834 (2004) | |
| Complete preprint article with high-resolution figures: | gzipped postscript (3.7 MB) | pdf (4.6 MB) |
| High-resolution version of Fig. 5 and Fig. 13 included in the astro-ph version: | Fig. 5 (gzipped postscript, 1.8 MB) | Fig. 13 (gzipped postscript, 1.6 MB) |
|
Please note that the results of this study were obtained
with calculations that did not incorporate general relativistic effects
and deleptonization during collapse. Recent
results by
Ott et al. (2006c)
and Dimmelmeier et al. (2006)
suggest that deleptonization and general relativity
have a significant quantitative and qualitative effect on the
gravitational wave signature of rotating core collapse.
Below we provide the gravitational wave signature data of all our models. The files are named according to the following nomenclature: | |||
|
[initial model name]A[value of A in km]B[value of initial beta=T/|W| in percent] |
|||
Where beta is the initial ratio of rotational kinetic to gravitational potential energy and A controls the degree of differential rotation in the rotation law | |||
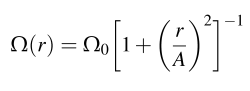
| |||
| in which r is the distance from the rotation axis. For example, setting A to 500 km leads to approximately solid body rotation within 500 km of the rotation axis. For more details please see the discussion in our paper. | |||
| We provide two types of data files. Files ending with .trh contain time (in seconds), maximum density (in g/cm^3), and dimensionless gravitational wave strain data (scaled to 10 kpc distance). The files ending with .spect contain the gravitational wave energy spectra in units M_sun c^2 / Hz. | |||
| 11 solar mass initial model (s11 from Woosley & Weaver 1995, ApJS 101, 181) | Summary Table | Individual model data files | Complete set of model data files: s11complete.tar.gz |
| 15 solar mass initial model (s15 from Woosley & Weaver 1995, ApJS 101, 181 ) | Summary Table | Individual model data files | Complete set of model data files: s15complete.tar.gz |
| 20/25 solar mass initial model (s20 from Woosley & Weaver 1995, ApJS 101, 181) | Summary Table | Individual model data files | Complete set of model data files: s20complete.tar.gz |
| Models from Heger 2000, ApJ 528, 368 and Heger et al. 2003, Stellar Rotation, Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 215 |
Summary Table | Individual model data files | Complete set of model data files: hegercomplete.tar.gz |